Greenhouse gases trap the sun's rays within the Earth's atmosphere and are considered one of the main culprits behind global warming Humans contribute to the increasing concentration ofThis warms Earth's atmosphere, making our planet habitable;Increases in all three gases contribute to warming of Earth, with the increase in CO 2 playing the largest role See page to learn about the sources of human emitted greenhouse gases Learn about the sources of human emitted greenhouse gases Figure b3

Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
Global warming greenhouse gases diagram
Global warming greenhouse gases diagram-Also methane, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Possible implications of increased greenhouse effect Junior Cycle Science Earth and space Sustainability 3 'Greenhouse' gases carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, water vapour effectively prevent some of this longwave radiation from leaving the atmosphere;
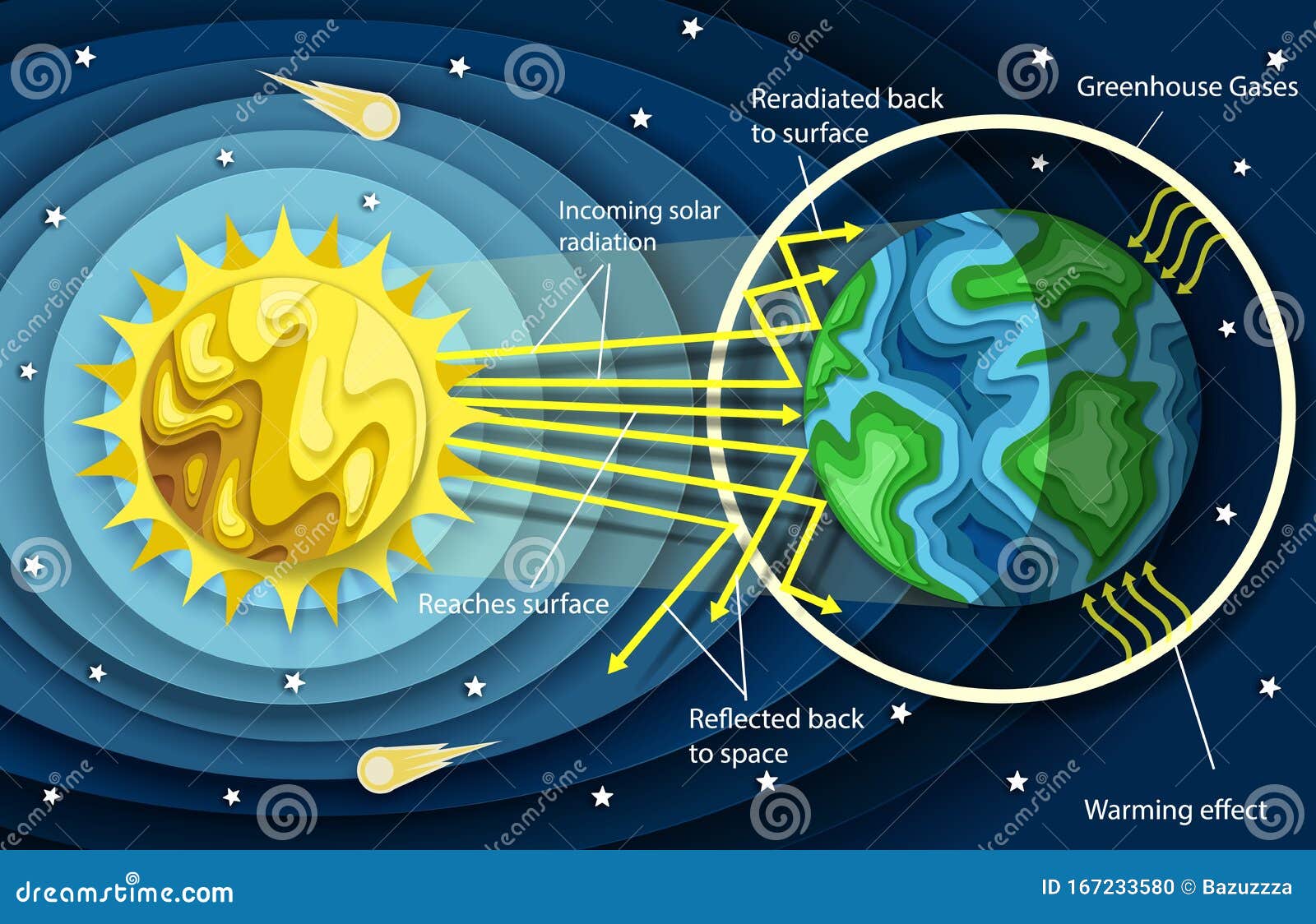



Vector Layered Paper Cut Style Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Ozone Greenhouse
Simplified diagram showing how Earth transforms sunlight into infrared energy Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane absorb the infrared energy, reemitting some of it back toward Earth and some of it out into spaceIncreased greenhouse gases from human activities result in climate change and ocean acidification Climate change = ocean change The world's ocean is a massive sink that absorbs carbon dioxide (CO 2) Although this has slowed global warming, it is also changing ocean chemistry Climate change dramatically affects coral reef ecosystems The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric CO 2 This happens because the coal or oil
Global Warming is accepted as fact by most of the scientific community However, Greenhouse Warming is more controversial because it implies that we know what is causing the Earth to warm Although it is known for certain that atmospheric concentrations of these greenhouse gases are rising dramatically due to An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percentThe greenhouse effect and the influence of human activity on it Greenhouse gases and their relative effects especially carbon dioxide and water vapour;
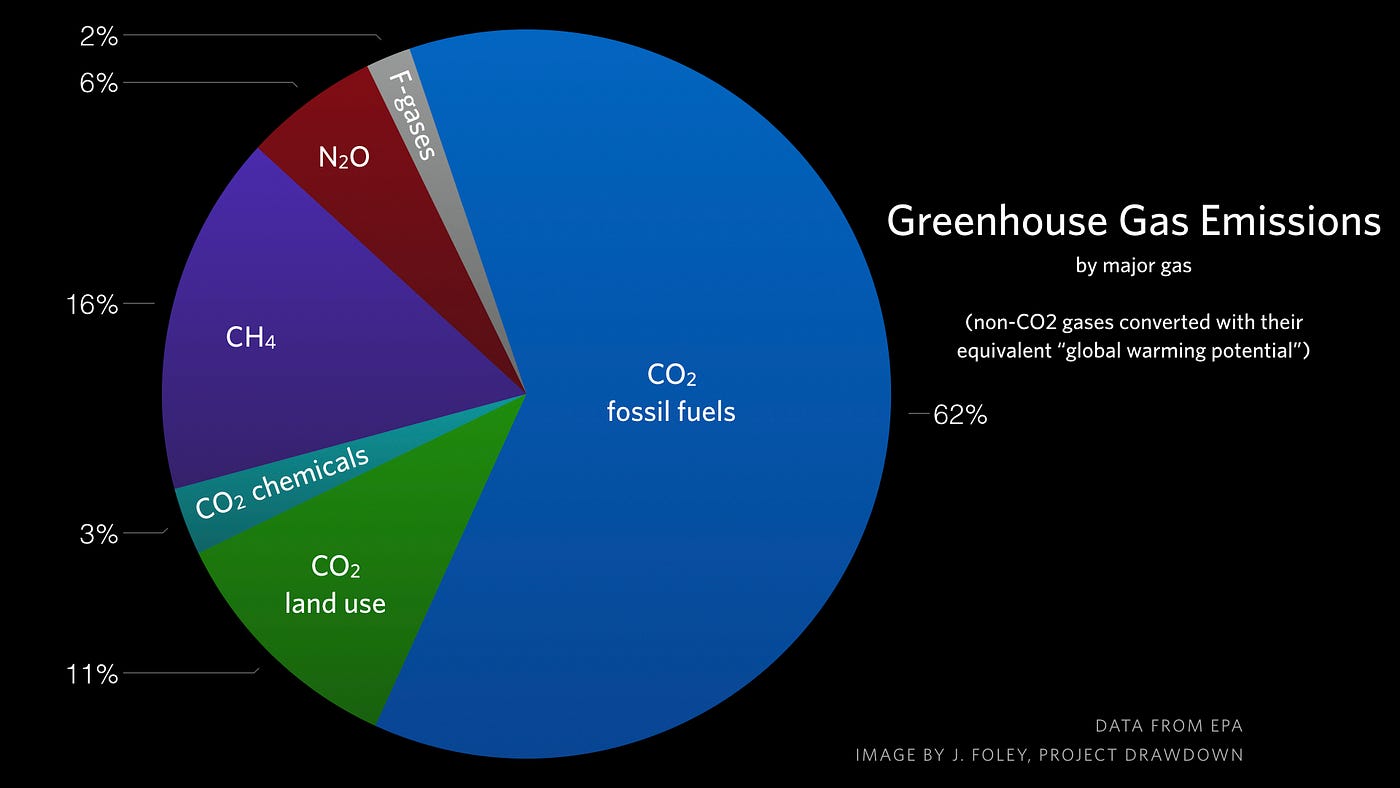
Anthropogenic global warming is a theory explaining today's longterm increase in the average temperature of Earth's atmosphere as an effect of human industry and agriculture For well over a century, scientists have been concerned that as the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases, so will the planet's capacity to retain heatThat approach in effect makes carbon dioxide, CO 2, the prevailing "currency" of greenhouse gases and global warming Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC)This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnes



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
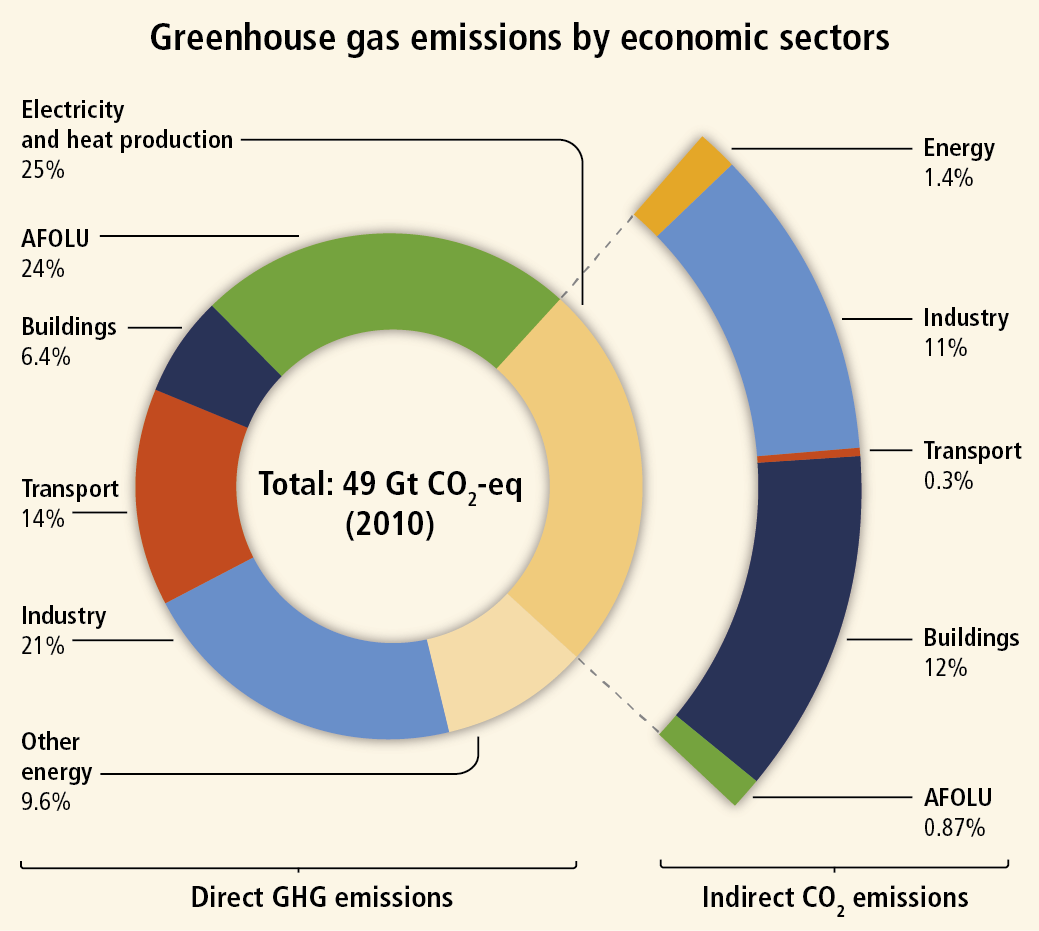
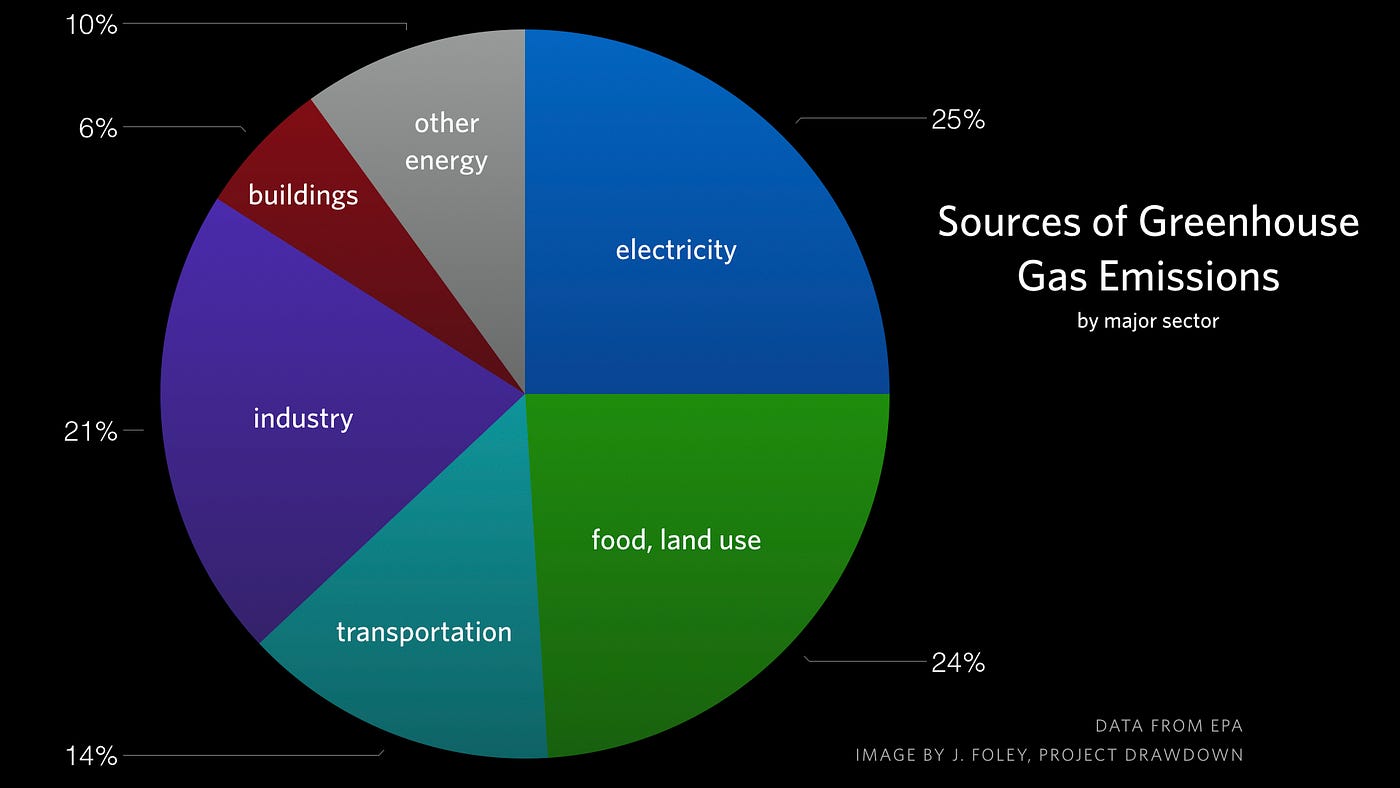
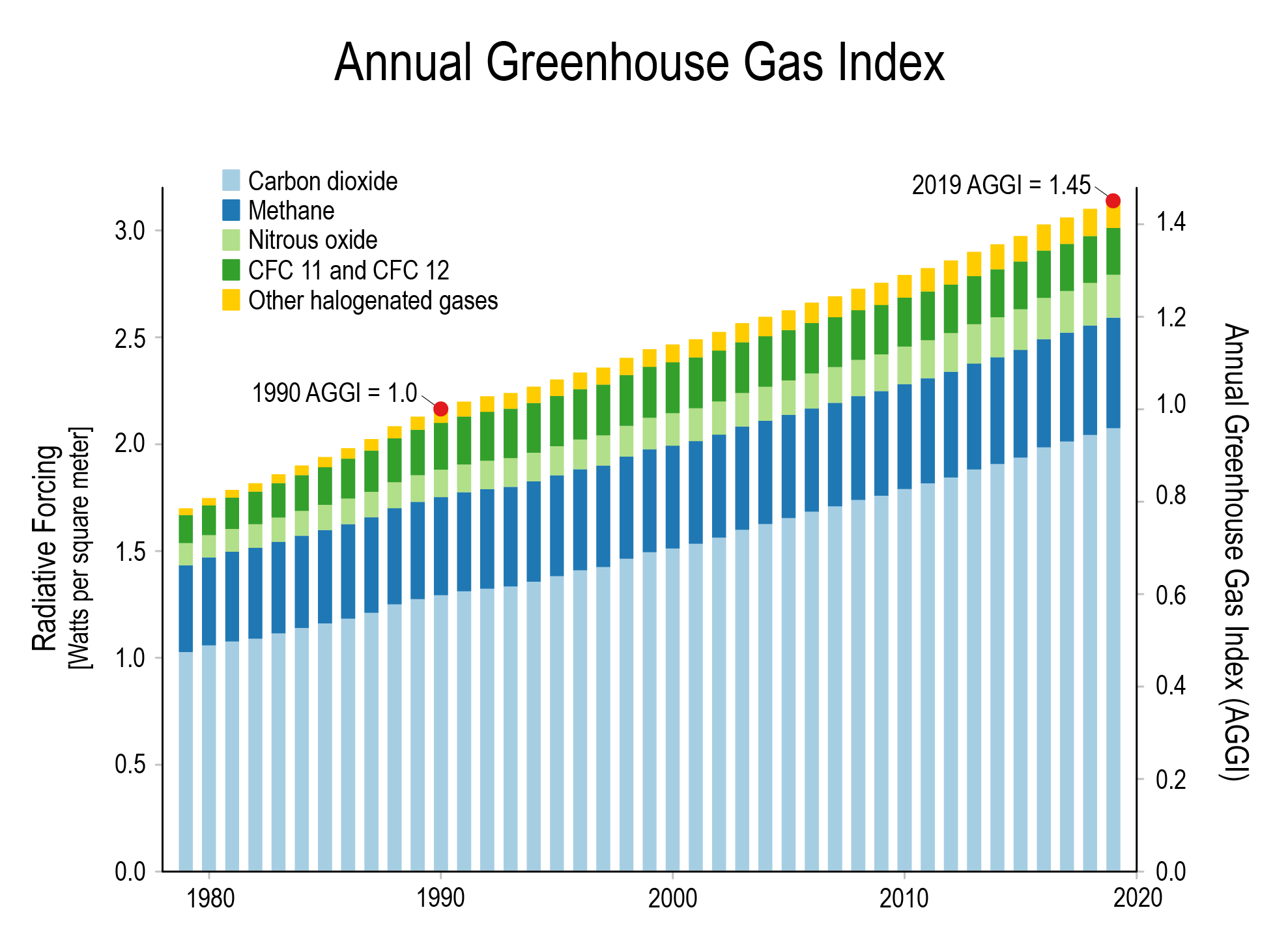
2 What do you think is meant by global warming? NOAA's Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI) is a yearly report on the combined influence of longlived greenhouse gases (atmospheric gases that absorb and radiate heat) on Earth's surface temperature The index compares the combined warming influence of these gases each year to their influence in 1990, the year that countries who signed the UN Kyoto Protocol Greenhouse Gas Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 2530% Futtsu Thermal Power Station near Tokyo Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels like coal, natural gas and oil produces more greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions than any human activity, accounting for at least one quarter of all global emissions




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
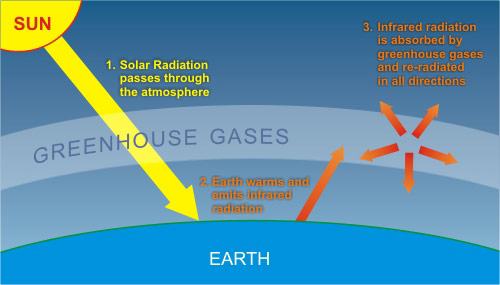
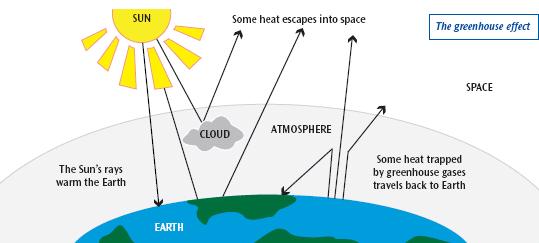
ESS3D Global Climate Change Human activities, such as the release of greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels, are major factors in the current rise in Earth's mean surface temperature (global warming) Reducing the level of climate change and reducing human vulnerability to whatever climate changes do occur depend on the understanding of climate science, engineeringAs a result, average surface temperatures are rising Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They let




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




How Exactly Does Carbon Dioxide Cause Global Warming You Asked
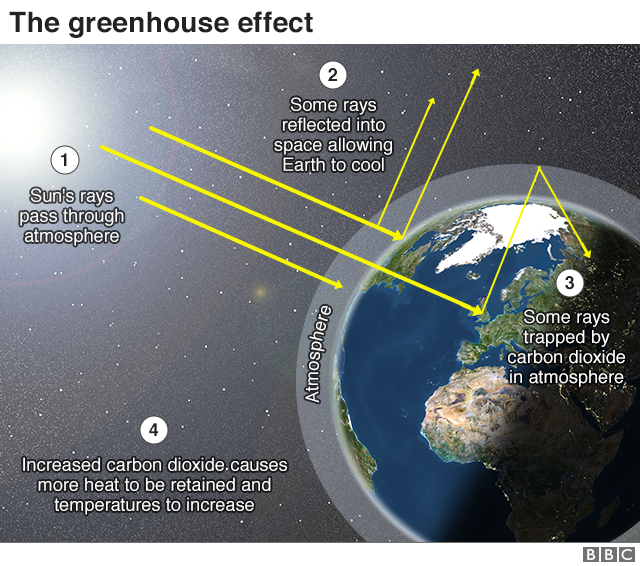
The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereThe greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Analyze global warming diagrams and resources to obtain a clear understanding of this scientific process 4 Hypothesize about the effects of global warming on the climate and the world's populations 5 Conduct research using a variety of primary sources to explore perspectives in the global warmingHuman activities have led to a build up of extra greenhouse gases in the atmsophere;




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change



Environment For Kids Global Warming
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclearCarbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas you hear people talk about the most That's because we produce more carbon dioxide than any other greenhouse gas, and it's responsible for most of the warming Some greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for only a short time, but others can stay in the atmosphere and affect the climate for thousands of yearsCarbon dioxideequivalents try to sum all of the warming impacts of the different greenhouse gases together in order to give a single measure of total greenhouse gas emissions To convert nonCO 2 gases into their carbon dioxideequivalents we multiply their mass (eg kilograms of methane emitted) by their 'global warming potential' (GWP)



c News



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change
Global warming is the increase in the average measured temperature of the Earth's nearsurface air and oceans since the midth century, and its projected continuation In media, it is synomonous with the term "climate change Global surface temperature increased 074 ± 018 °C during the 100 years ending in 05The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)The greenhouse effect has supported life on the earth for millions of years Today, however, the greenhouse effect is growing stronger as human activities such as deforestation and fossil fuel use release more and more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere This traps greater amounts of the sun's radiation, which contributes to rising temperatures, also known as global warmingGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, methane, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and water Show that you understand the greenhouse effect by cutting out the labels and sticking them on to the diagram below Questions 1 If the greenhouse effect did not exist, what would the normal temperature of the earth be?




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




Contribution From Different Greenhouse Gases To The Global Warming Download Scientific Diagram
Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16° F) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearly doubled in the last 50 yearsThese characteristics are incorporated in the Global Warming Potential (GWP), a measure of the radiative effect (ie the strength of their greenhouse effect) of each unit of gas (by weight) over a specified period of time, expressed relative to the radiative effect of carbon dioxide (CO 2) This is often calculated over 100 years, though it can be done for any time periodGreenhouse Gas Induced Global Warming Since the industrial revolution got into full swing in the 19th century we have been burning ever increasing amounts of fossil fuels (coal, oil, gasoline, natural gas) in electric generating plants, manufacturing plants, trains, automobiles, airplanes, etc Burning releases CO 2 into the atmosphere (much the same as respiration does)



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an important heattrapping (greenhouse) gas, which is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, as well as natural processes such as respiration and volcanic eruptionsThe first graph shows atmospheric CO 2 levels measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, in recent years, with average seasonal cycleGreenhouse gas emissions are often measured in carbon dioxide (CO 2) equivalent To convert emissions of a gas into CO 2 equivalent, its emissions are multiplied by the gas's Global Warming Potential (GWP) The GWP takes into account the fact that many gases are more effective at warming Earth than CO 2, per unit massThese greenhouse gases are used in aerosol cans and refrigeration All of these human activities add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, trapping more heat than usual and contributing to global warming Effects of Global Warming Even slight rises in average global temperatures can have huge effects



What Is Climate Change And How Will It Affect The Uk Bradford Council




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
"Global warming" refers to the rise in global temperatures due mainly to the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere "Climate change" refers to the increasing changes in the measures of climate over a long period of time – including precipitation, temperature, and wind patternsGuest post by Kevin Judd Climate scientists are telling us that gases like carbon dioxide are causing global warming Carbon dioxide is produced when petrol is burned in your car engine, or when coal and gas are burned at powerstations to make electricity Carbon dioxide causes global warming because it contributes to the socalled greenhouse effect Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect En la gráfica se comparan los cambios en la temperatura de la superficie global (línea roja) y la energía del Sol que recibe la Tierra (línea amarilla) en vatios (unidades de energía) por metro cuadrado desde 10



Impact Of Agriculture On Climate Change



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News
Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphereGlobal warming is an aspect of climate change, referring to the longterm rise of the planet's temperatures It is caused by increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, mainly from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation and farming 1 Burning fossil fuels When we burn fossil fuels like coal, oil and This resource focuses on the the greenhouse effect and five human causes of global warming Content A look at the greenhouse effect at a range of scales The macro scale factors that are increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere A consideration of what/who is to blame and how these sectors may change in the future Resources are




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
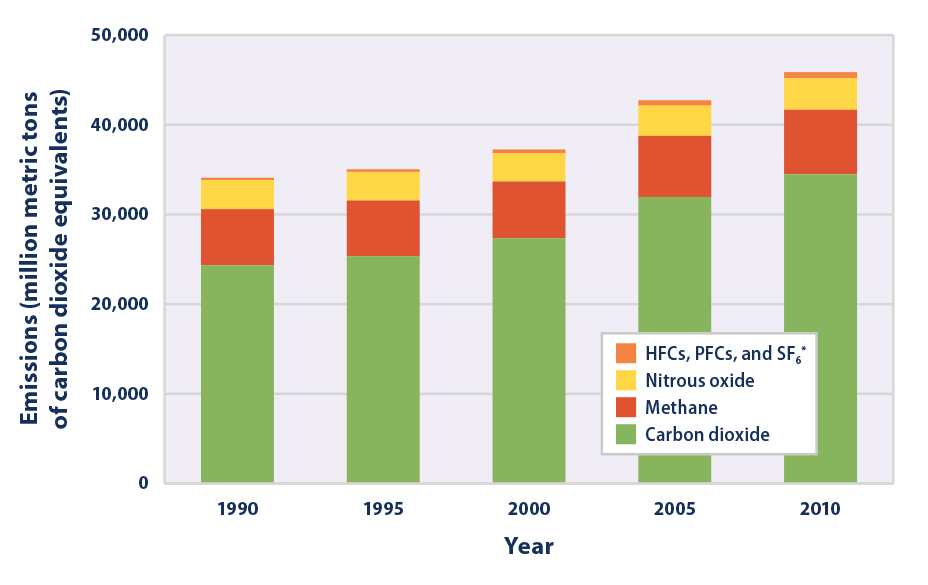
Global warming refers to the longterm rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate systemIt is a major aspect of climate change, and has been demonstrated by the instrumental temperature record which shows global warming of around 1 °C since the preindustrial period, although the bulk of this (09 °C) has occurred since 1970 A wide variety of temperature proxiesMedia in category "Global warming diagrams" The following 106 files are in this category, out of 106 total 19 Academic studies of scientific consensus global warming, climate changeensvg 725 × 375;The Kyoto Protocol applied to the seven greenhouse gases listed in Annex A carbon dioxide (CO 2), Methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6), Nitrogen trifluoride (NF 3) Nitrogen trifluoride was added for the second compliance period during the Doha Round




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org
The "Greenhouse Gases" students should then each trap one "Heat" student Since there are many more Greenhouse Gases, more "Heat" will be trapped on Earth, with very little, if any, "Heat" escaping This is how global warming happens At the end of the activity, bring the learners back together as a group and discuss what they learnedThere are many greenhouse gases but these are some of the most important water vapour, H2O carbon dioxide, CO2 methane, CH4 nitrous oxide, N2O CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons)




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
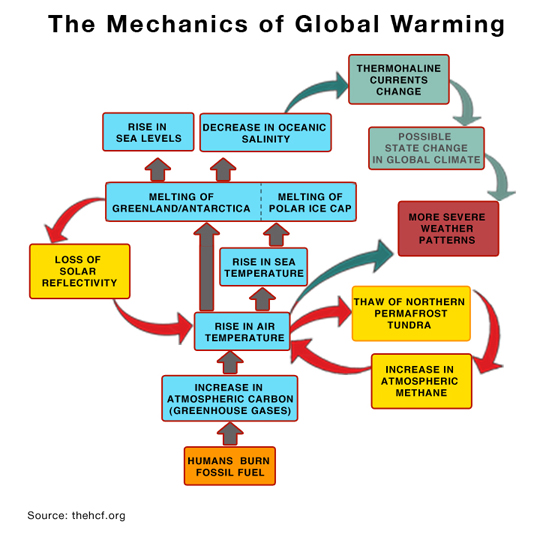



Report 3 How Do Greenhouse Gases Cause Global Warming Hinkle Charitable Foundation



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Understanding The Greenhouse Effect Sciencemusicvideos




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education
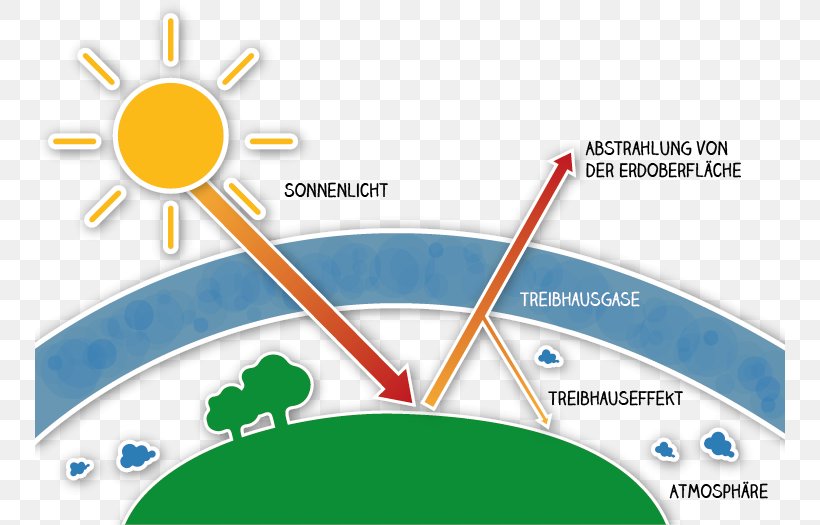



Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Anthropogen Global Warming Png 750x525px Greenhouse Effect Area Atmosphere Of




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



1




Greenhouse Effect Vs Global Warming Reading And Diagram 6 8 Ngss




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




The Discovery Of Global Warming International Brotherhood Of Boilermakers
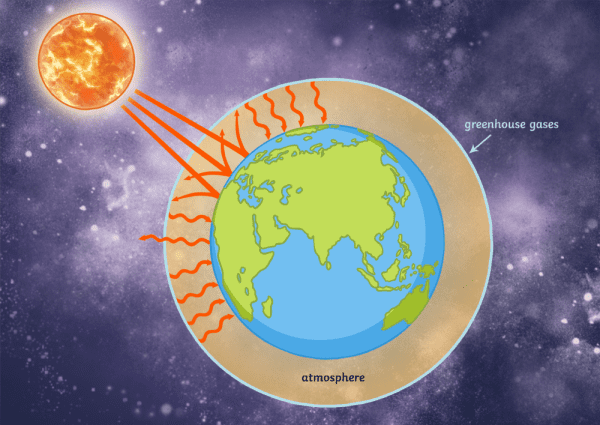



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Vector Layered Paper Cut Style Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Ozone Greenhouse




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
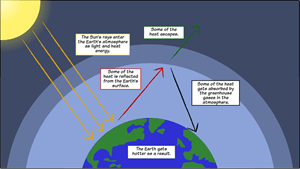



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan



1




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
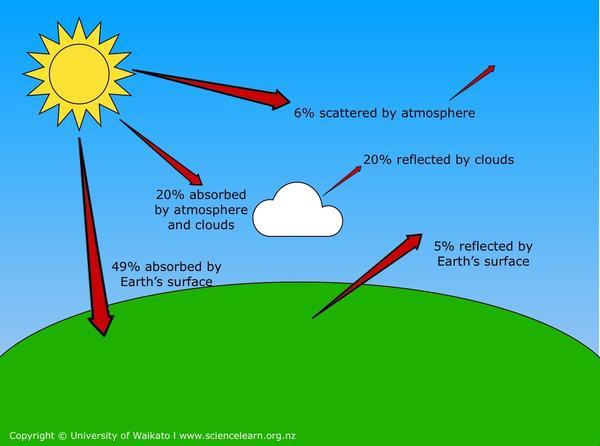



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov



Global Warming
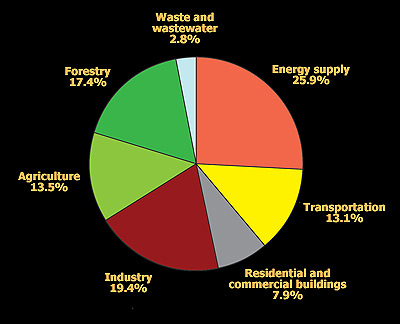



Tackling The Global Warming Challenge



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




Global Warming



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Global Warming Naturally Existing Greenhouse Gases Trap The Part Of Download Scientific Diagram




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
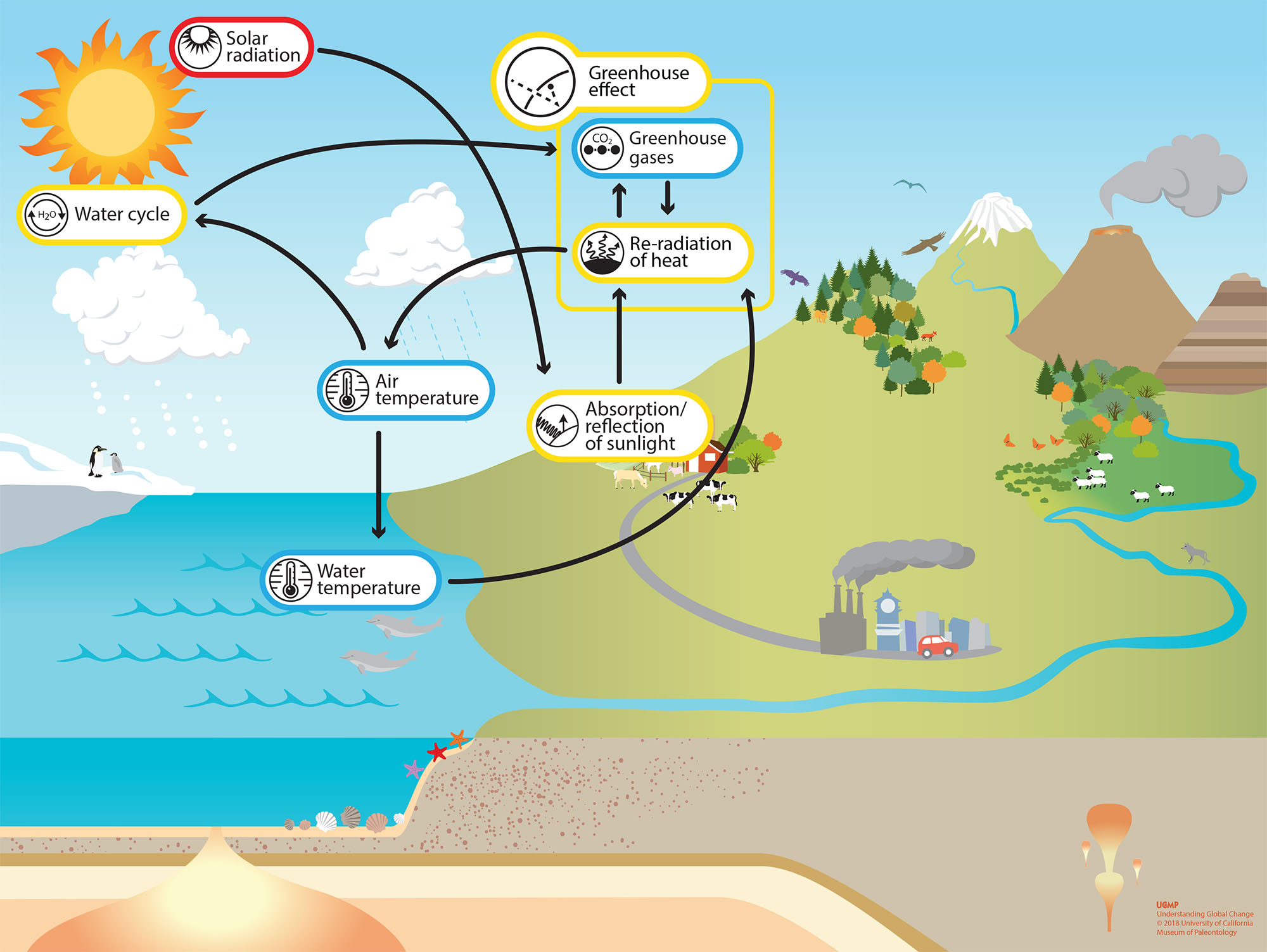



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




Direction Using A Venn Diagram Below Compare Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Brainly Ph
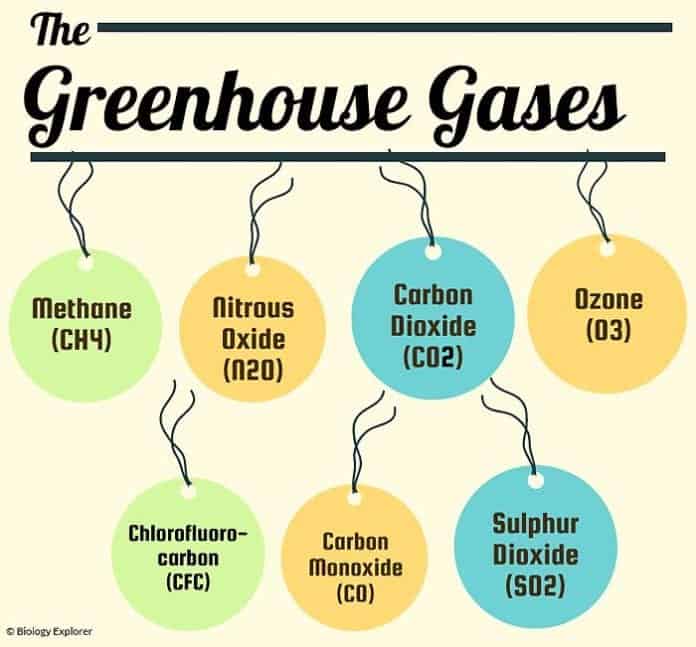



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science
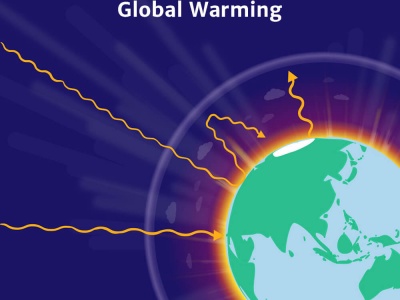



The Greenhouse Effect Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
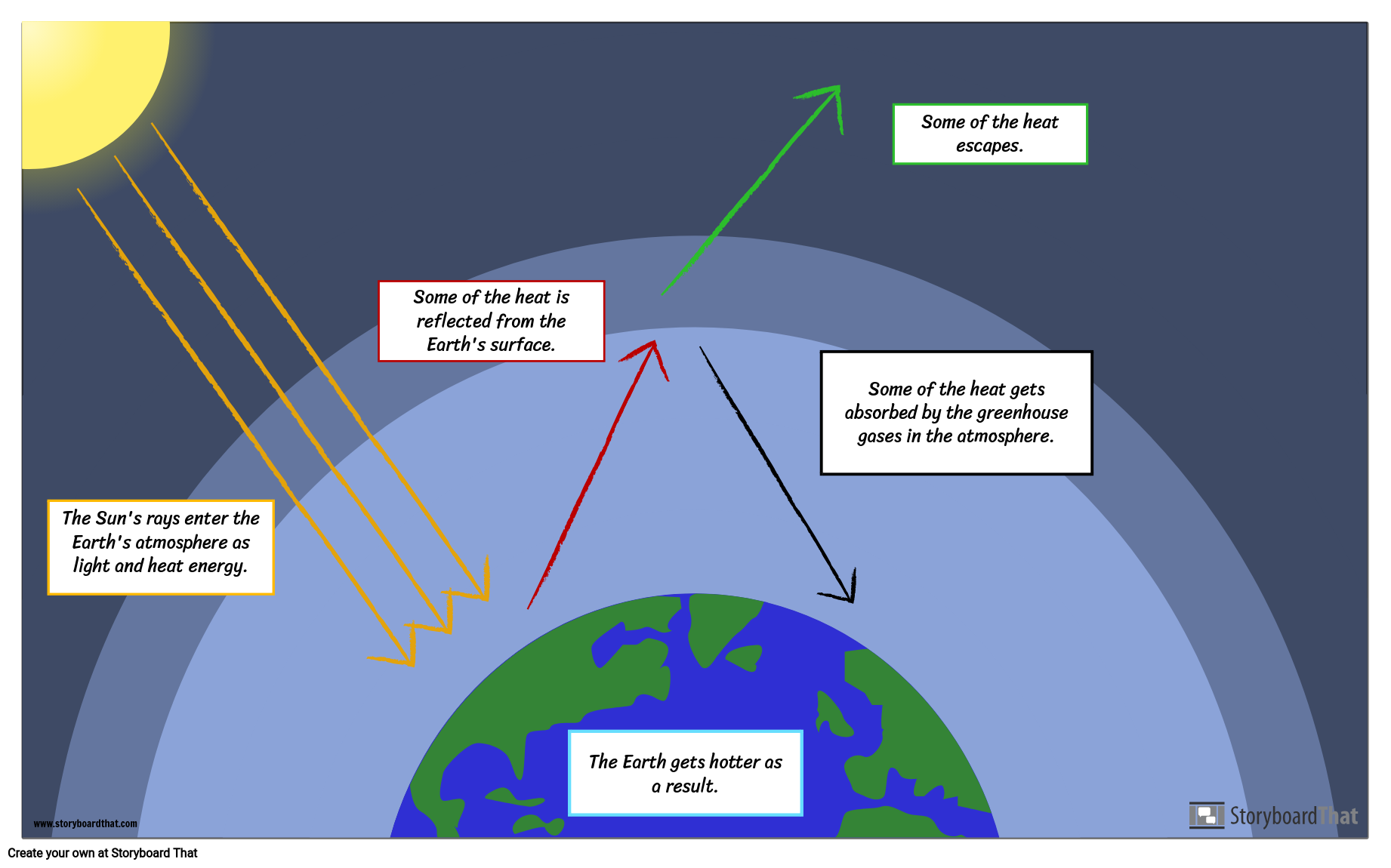



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



1




The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Warming Global New Light Of Myanmar




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate




Brizz Grafixx Global Warming



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




4 2 The Greenhouse Effect A Biology



Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre
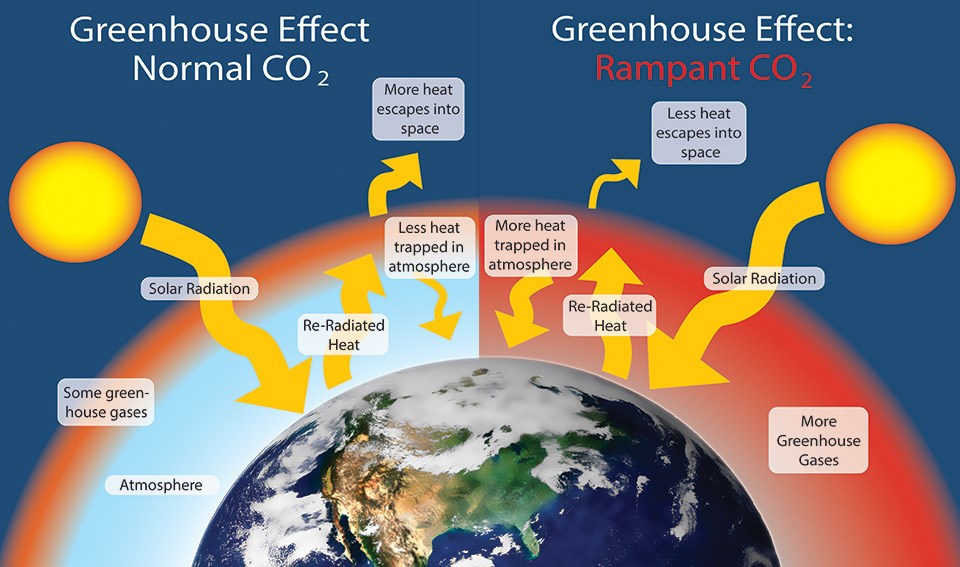



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service




Climate Change And Global Warming Center For The Study Of The Built Environment
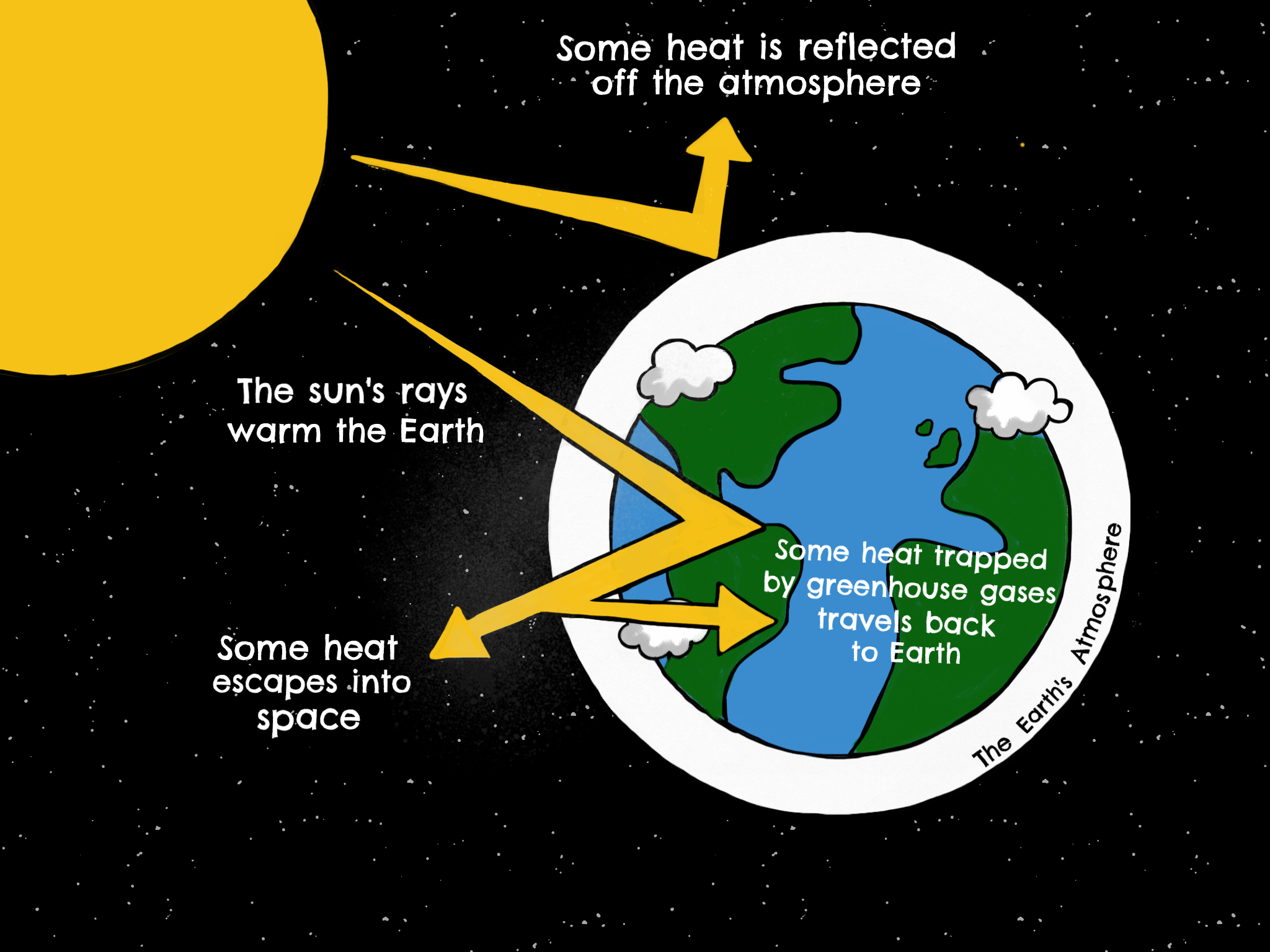



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Natural And Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing Solar Radiation And Planet Earth Global Warming Climate Change Canstock




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
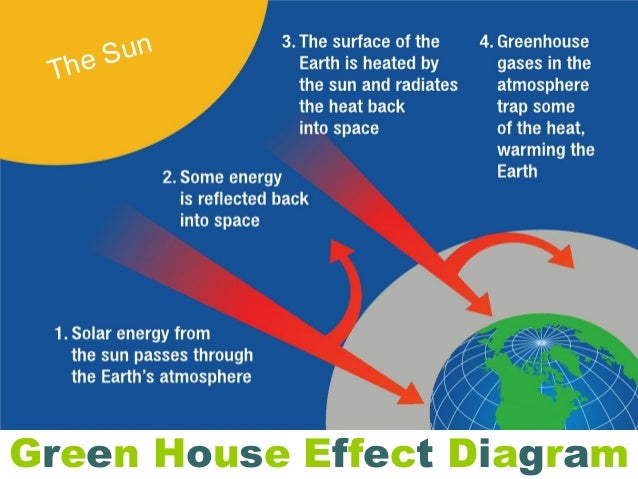



Global Warming And Green House Effect
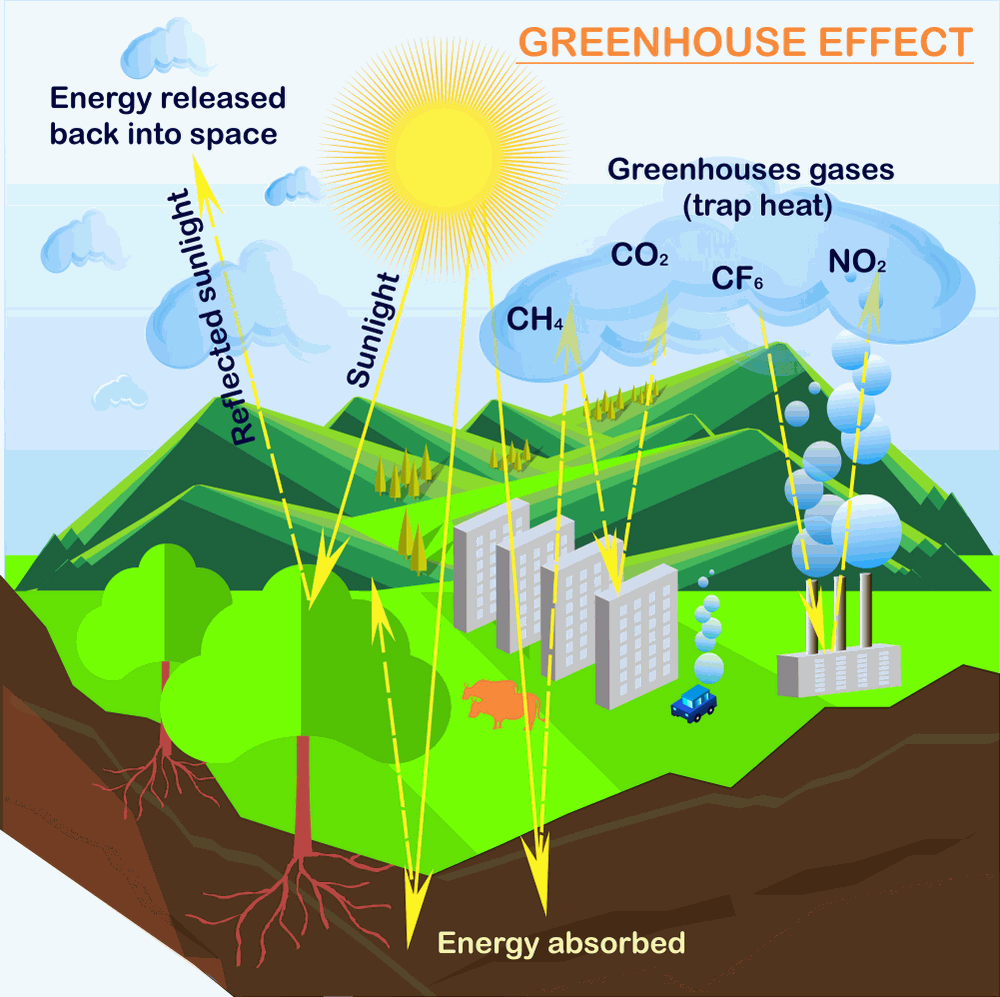



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Introduction To Air Pollution Air Pollution Issues




Causes And Consequences Of A Warming Planet Agricultural Marketing Resource Center




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases




Global Warming Key Driver Of 15 S Record Heat Climate Central




The Greenhouse Effect Experiment And Lesson For Kids




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic By Mind The Graph The Science Educator Medium



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut
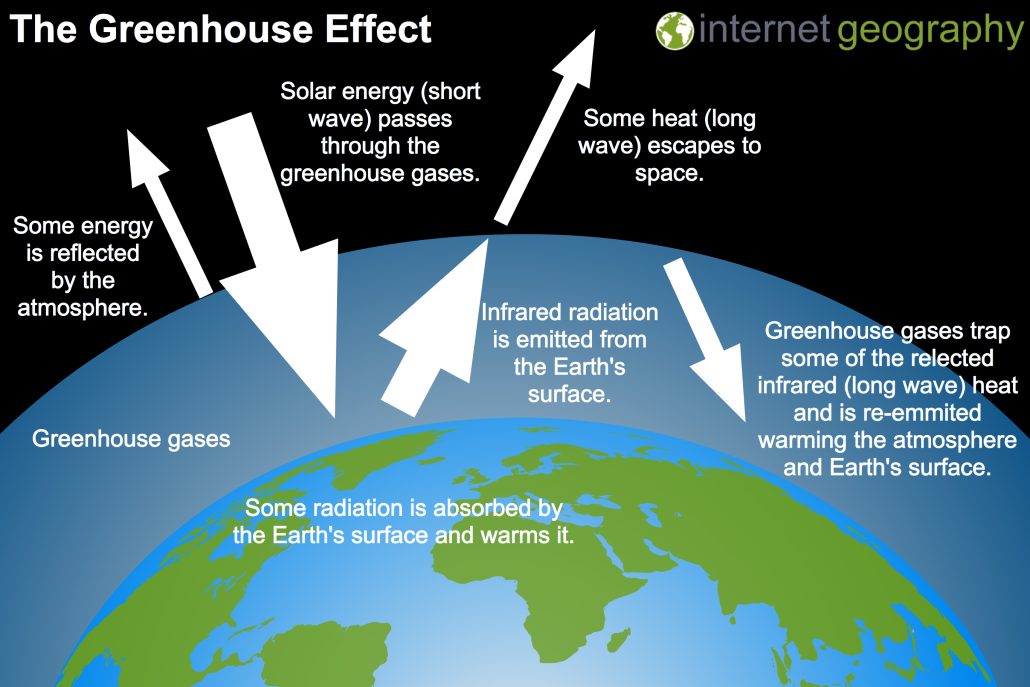



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
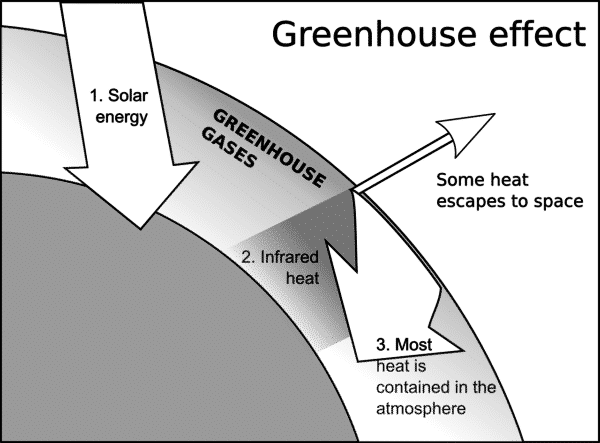



What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia



Greenhouse Gases
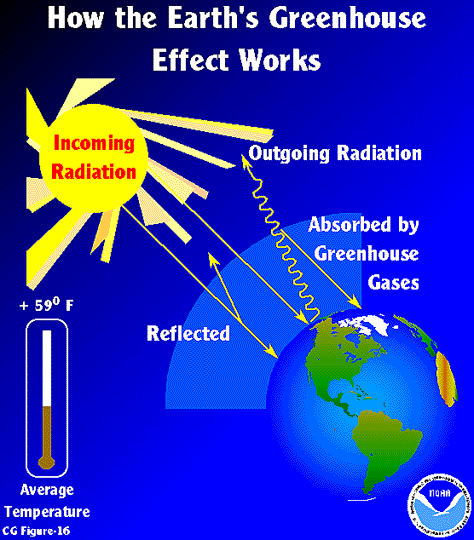



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
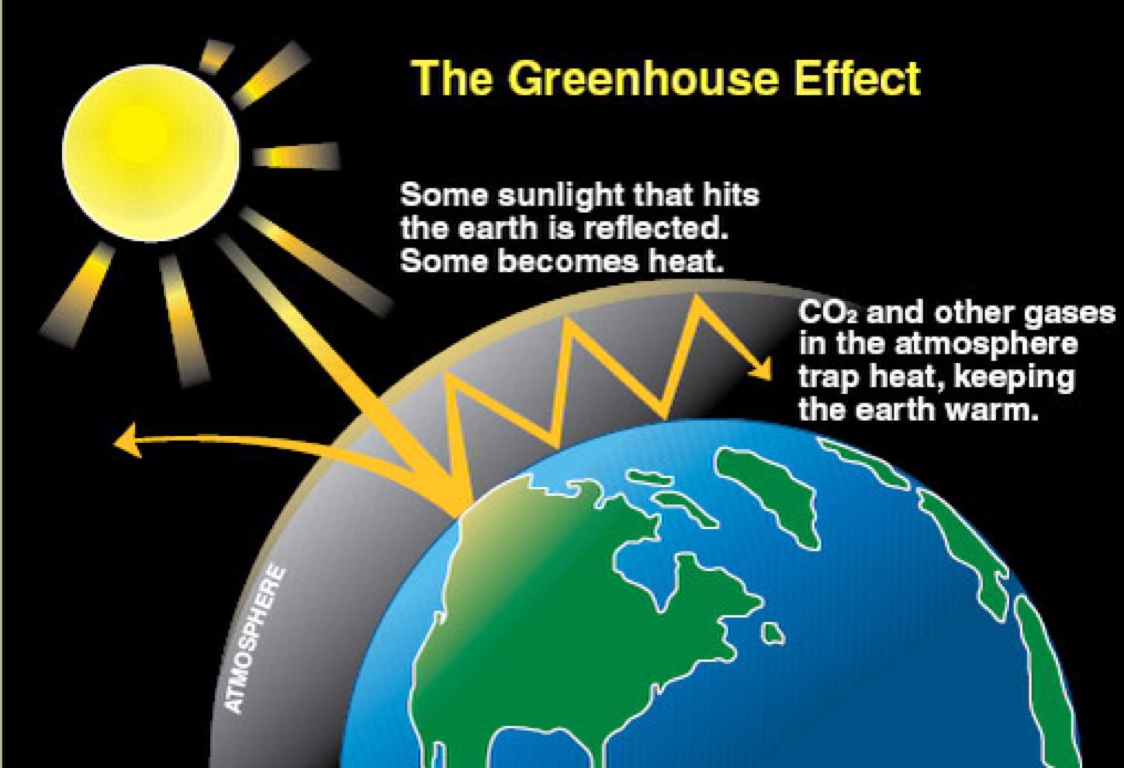



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic
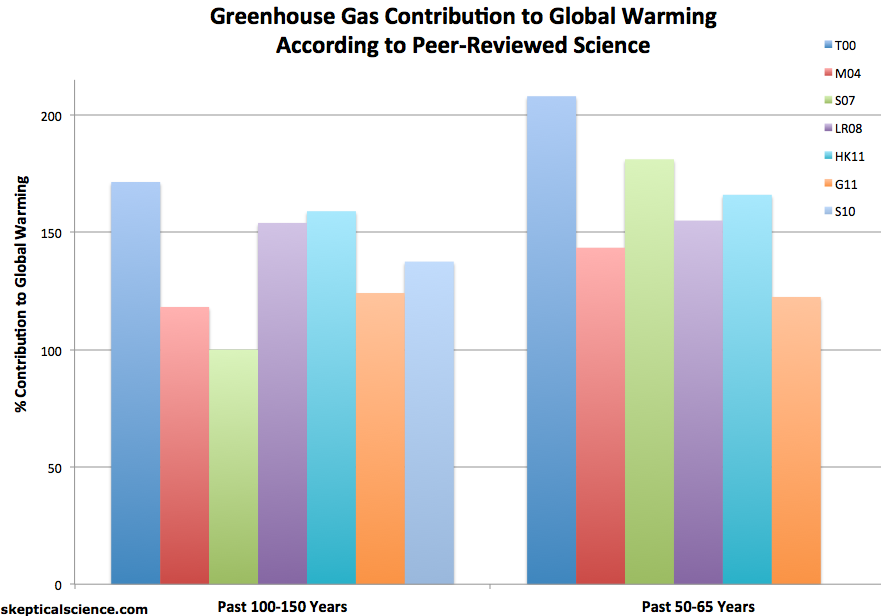



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing How The Greenhouse Effect Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Climate Change Diagram Quizlet




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
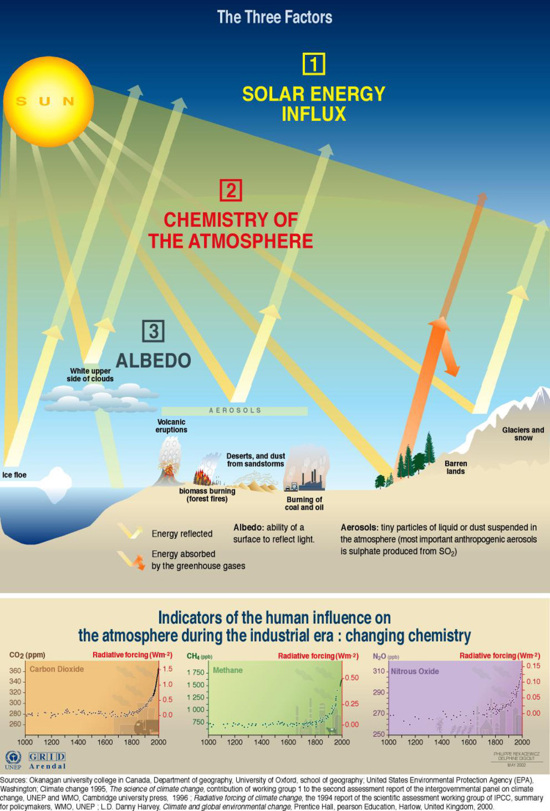



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal


